Introduction to Fine-Particle Bombarding Service
Micro-particle modification technology differs from traditional sandblasting processes by utilizing ultra-fine, high-toughness, and high-hardness powders, which are sprayed onto metal surfaces using high-pressure equipment. This method creates fine dimple structures that enhance the material's strength without damaging precision tools or molds.
Micro-particles, when impacting a metal surface at high speeds, generate significant compressive residual stress (greater than -1,400 MPa), which enhances the fatigue strength and surface wear resistance of metal components.
Micro-particles create fine pit features (less than 2 micrometers) on the metal surface, which preserve the lubricating oil film, reduce the coefficient of friction, and enhance release properties. This process improves coating adhesion and extends the service life of molds.
This technology has been developed over the past decade in Switzerland, Germany, and Japan, and is utilized in aerospace, precision molds, and medical equipment components.
Mechanisms of Metal Fatigue and Wear
The primary cause of metal wear damage is the impact of repeated cyclic stresses, whether thermal or mechanical, on the metal surface. Consequently, when the surface of an object is rough or contains micro-defects in the inner layer, it can result in material degradation and fracturing due to fatigue stress.
The fastest and most effective method for improvement is to apply pre-compressive stress to the surface, counteracting the effects of fatigue stress on tools or molds during the production process.
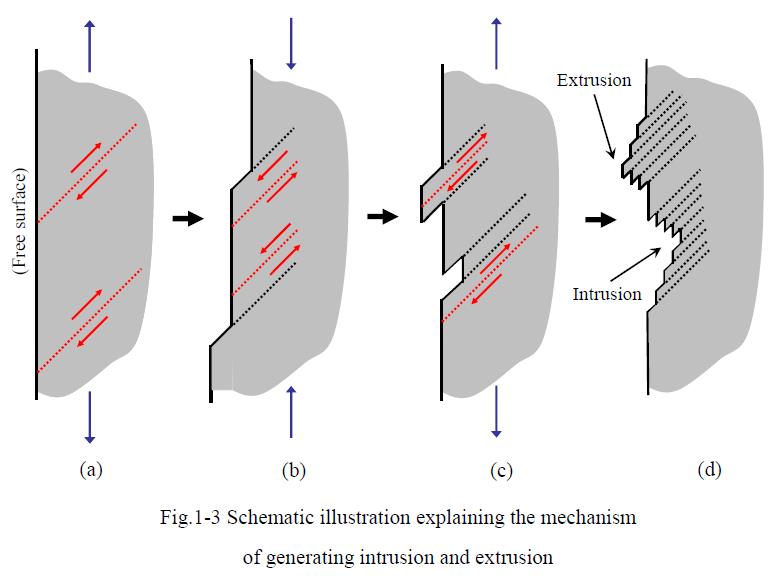
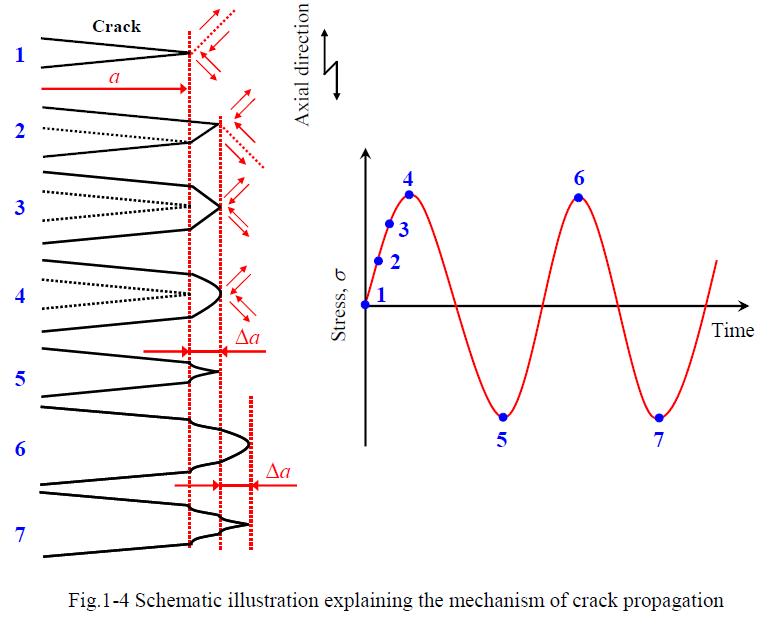
▲Fatigue Crack Growth
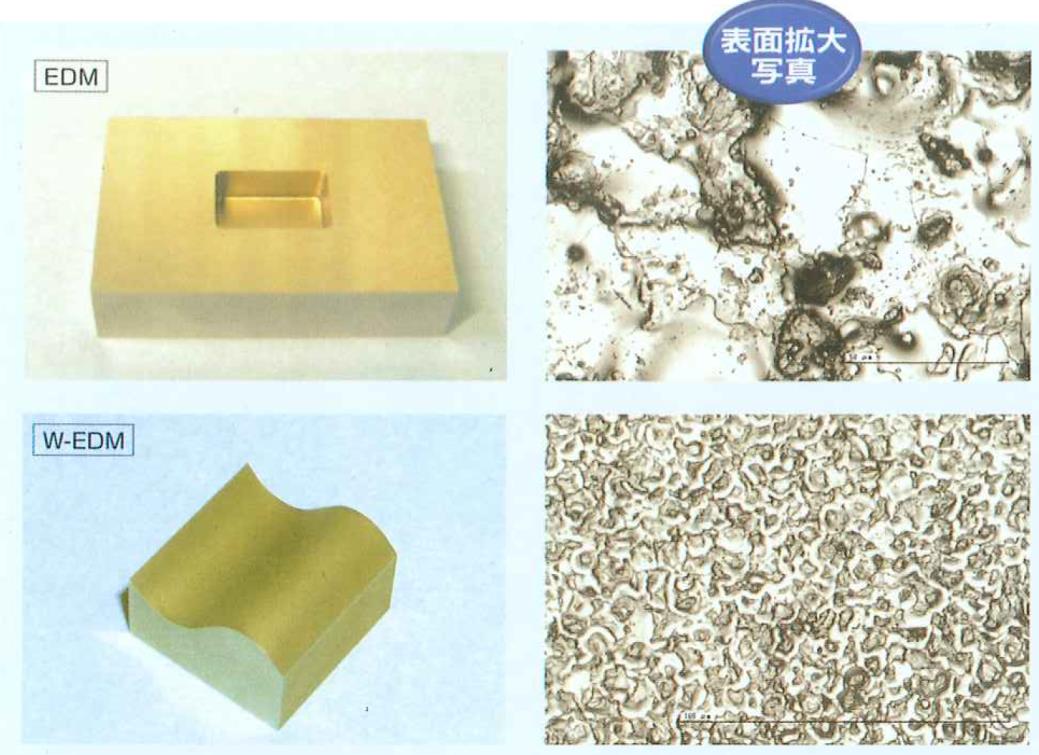
Metal Processing Surface Quality Problem Points
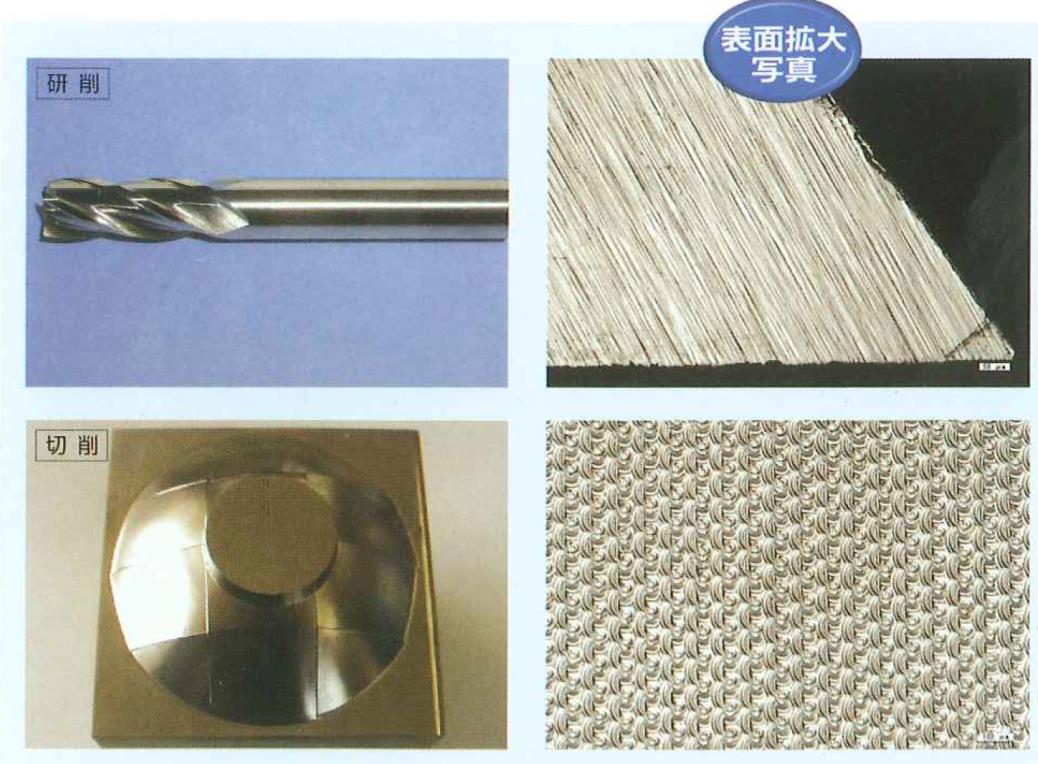

Principle of the Technology
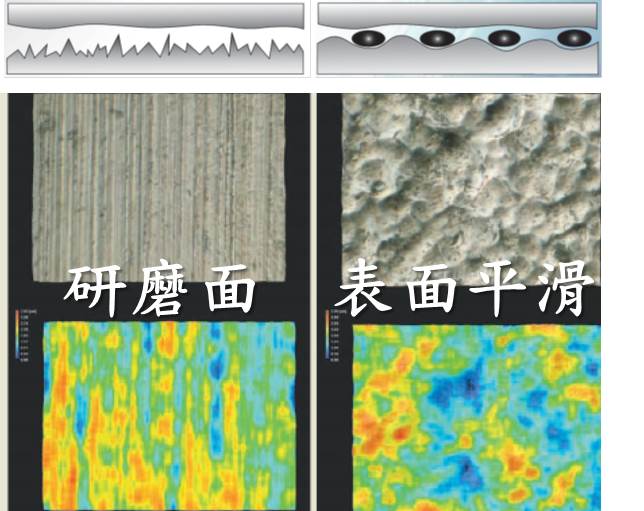
▲Before (left image) and after (right image) treatment comparison.
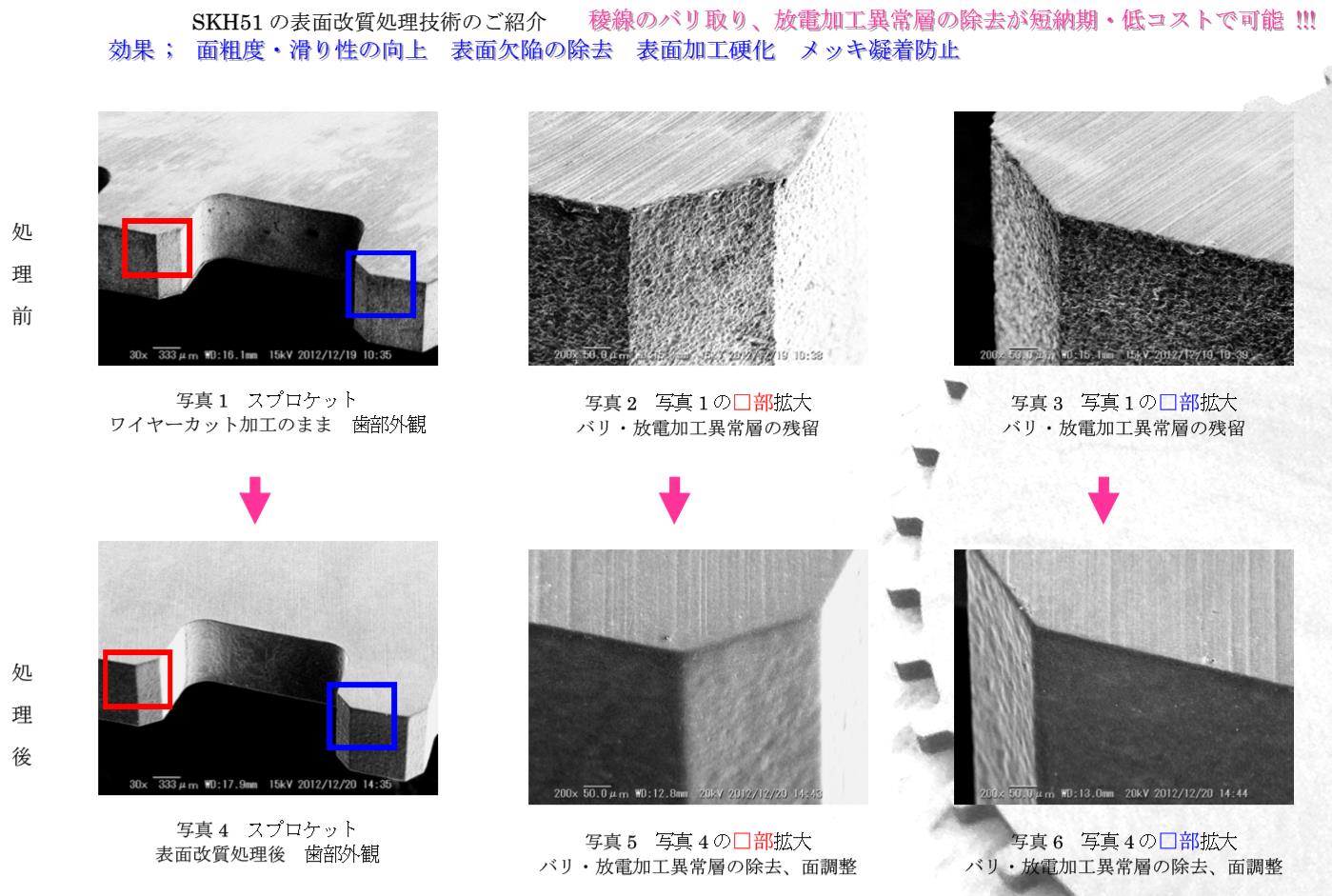
▲Before (top image) and after (bottom image) treatment comparison.
Features of Metal Surface Modification Technology
Effects of Metal Surface Modification Technology
Application Cases of Metal Surface Modification Technology
Widely used in the fields of mechanical components, cutting tools, mold parts, and more.
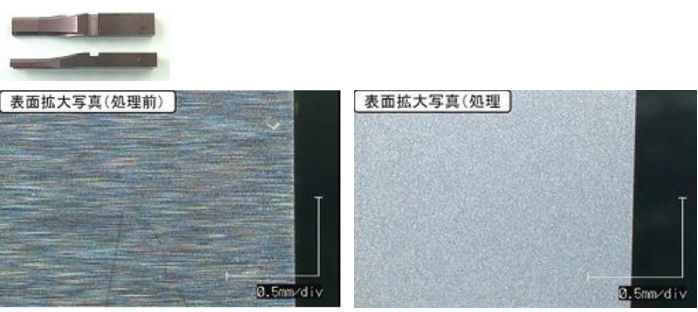
▲A comparison of the wire rack punch surface modification before (first image) and after (second image) treatment.
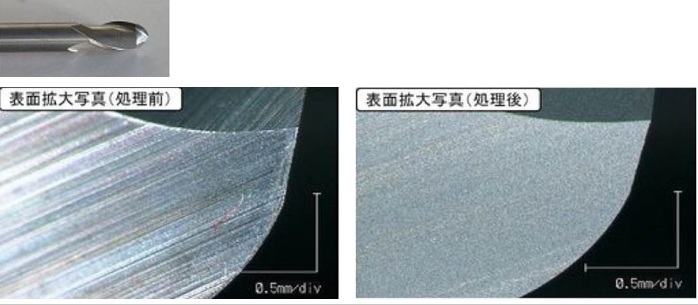
▲A comparison of tungsten steel end mill surface modification before (first image) and after (second image) treatment.
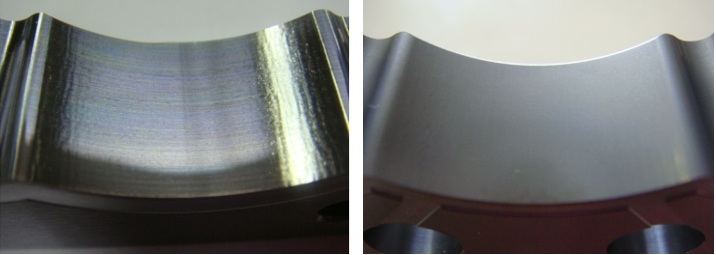
▲A comparison of the extrusion mold surface modification before (first image) and after (second image) treatment.
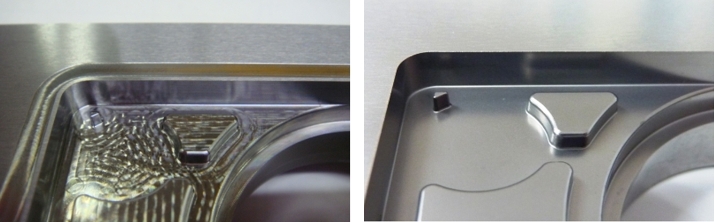
▲A comparison of plastic injection mold surface modification, showcasing the before (first image) and after (second image) treatment results.